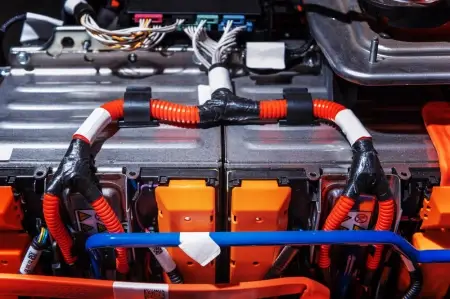
When we talk about electric cars, the first thing most people mention is the “electric motor” or the “no CO2 emissions ” . But what really gives life to these vehicles, what we could consider their “heart”, is the battery. Without the battery, there is no working electric car.
It's something like the gas tank in combustion cars, but at a much more advanced level. Today I'm going to tell you everything you need to know about electric car batteries, from how they work, to the different types that exist and their future.
What is an electric car battery?
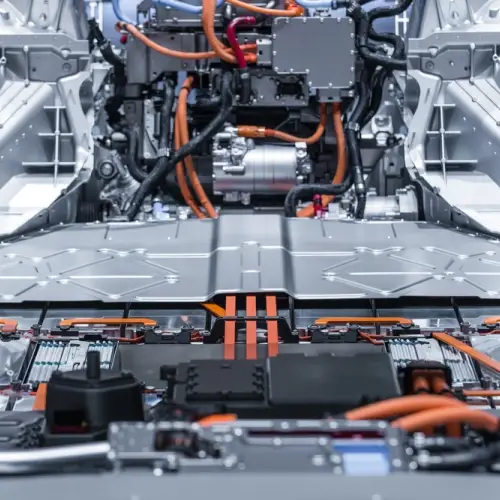 An electric car battery is a set of cells that store energy in the form of electricity and release it when needed. This process of storing and releasing energy is what allows the car to run, the engine to turn, and you to move.
An electric car battery is a set of cells that store energy in the form of electricity and release it when needed. This process of storing and releasing energy is what allows the car to run, the engine to turn, and you to move.
Batteries are nothing new, they've been around since Edison invented the first ones in the 19th century. However, electric car batteries are a more complex technology. While a battery like the one you use in your TV remote control has a limited capacity, an electric car battery must store enough energy to move a vehicle weighing more than a tonne at speeds that can exceed 150 km/h. No small feat.
Types of electric car batteries
In the electric car market, there are mainly two types of batteries: lithium-ion batteries and solid-state batteries . Separately, nickel-metal hydride batteries are widely talked about , but they are less common in new generation electric cars today. Let me explain each one:
Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries
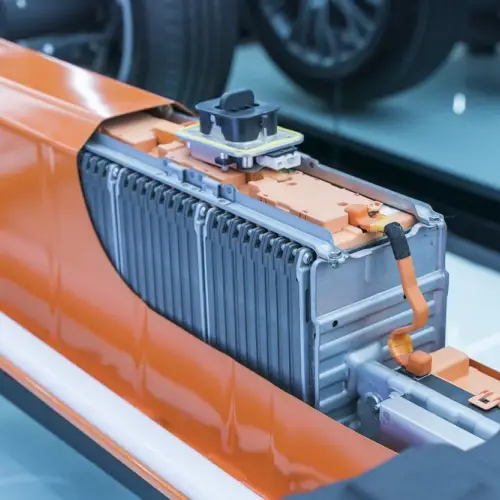 They are, without a doubt, the most common in electric cars today. They work by circulating lithium ions between the anode and the cathode of the battery. Their great advantage is that they have a high energy density, which means they can store a lot of energy in a small space. They are light and efficient.
They are, without a doubt, the most common in electric cars today. They work by circulating lithium ions between the anode and the cathode of the battery. Their great advantage is that they have a high energy density, which means they can store a lot of energy in a small space. They are light and efficient.
Most electric cars today, from the Tesla Model 3 to the Nissan Leaf, use these types of batteries. However, they also have some drawbacks, such as being sensitive to extreme temperatures (if it's too hot or too cold, they lose efficiency) and degrading over time.
Solid state batteries
Although they are still in the development phase and are not widely used in electric cars, they promise to revolutionise the industry. These batteries use a solid electrolyte instead of a liquid one, making them safer (there is no risk of leaks or fires) and with a higher energy density.
Compared to lithium batteries, solid-state batteries could offer much greater autonomy in the same space. The downside is that they are very expensive to produce and are not yet ready for the general public, but major brands such as Toyota and Volkswagen are already investing a lot of money in developing them.
Nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries
They were very popular in the first generation of hybrid cars, such as the Toyota Prius. Today, they are still used in some hybrids, but have been largely replaced by lithium batteries in fully electric cars. They are heavier and have a lower energy density, so manufacturers have somewhat neglected them for pure electric vehicles.
How do they work?
How an electric car battery works may seem complicated, but it's actually pretty simple when you boil it down to the basics. The car stores energy in the battery cells when you plug it into a power source, such as a charging station or the socket in your home. This energy is used by the electric motor when you step on the accelerator.
Inside the battery, chemical energy is converted into electrical energy through an electrochemical reaction. The resulting current is passed to the motor, which in turn drives the car's wheels. The whole process is silent, efficient and, most importantly, without any emissions of polluting gases.
Of course, battery performance depends on several factors: temperature, how you use the car and, of course, its age.
How long does an electric car battery last?
This is what many people are worried about: “How long will my battery last?” It’s a fair question, because replacing a battery isn’t cheap. The good news is that modern electric car batteries are designed to last a long time. Most manufacturers guarantee their batteries for 8 to 10 years or about 160,000 kilometers.
Of course, like any other battery, they lose capacity over time. For example, a battery that had a range of 400 km when it was new can lose 10-20% of its capacity after those 8-10 years. But it doesn't mean that the battery will suddenly "die". You will simply have to charge the car more frequently.
What causes batteries to degrade over time is primarily the number of charge cycles . A charge cycle is when you charge the battery from 0% to 100%. The more cycles you do, the faster the battery deteriorates. That's why many manufacturers recommend not always charging it to 100% and avoiding fully discharging it.
Autonomy: how many kilometers can I go on a single charge?
 Range is certainly one of the biggest concerns when buying an electric car. And it makes sense, because one of the big advantages of combustion cars is that you can find a gas station almost anywhere. With an electric car, the charging infrastructure is growing, but it is not as widespread as traditional gas stations.
Range is certainly one of the biggest concerns when buying an electric car. And it makes sense, because one of the big advantages of combustion cars is that you can find a gas station almost anywhere. With an electric car, the charging infrastructure is growing, but it is not as widespread as traditional gas stations.
As for autonomy, it depends on several factors:
- Battery size : The larger the battery, the greater the range of the car. A Tesla Model S, which has a battery of more than 100 kWh, can travel about 600 km on a single charge. A smaller car, such as the Renault Zoe, has a range of about 300 km.
- Driving conditions : If you drive at high speeds on the motorway, the battery will drain faster. The same is true if you have the air conditioning or heating on. In normal city conditions, where speeds are lower, the range is usually better.
- Climate : Extreme cold weather negatively affects lithium-ion batteries. If you live in an area with very cold winters, you will notice a drop in battery life during those months. Very high temperatures can also affect the battery, but not as much as the cold.
Loading time
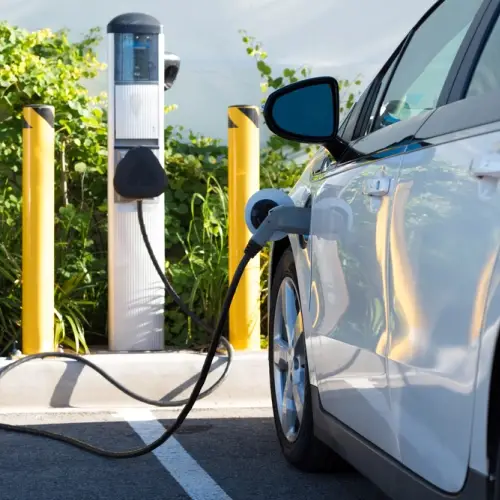 Another very common question: "How long does it take to charge?" The answer here depends on the type of charger you use.
Another very common question: "How long does it take to charge?" The answer here depends on the type of charger you use.
- Home charging (Wallbox) : If you charge your car at home using a wallbox charger, which is the most common choice for electric car owners, the charging time depends on the power of your installation. On average, a full charge can take between 5 and 8 hours. It's ideal to charge it overnight and have the car ready in the morning.
- Fast chargers : If you use a fast charger, which you can find at gas stations or public charging points, you can charge up to 80% of the battery in about 30-40 minutes. This is ideal for long trips, where you don't want to spend a lot of time charging.
- Ultra-fast charging : Some superchargers can charge the battery in less than 20 minutes, but not all cars are compatible with this type of charging. In addition, the network of ultra-fast chargers is still expanding, so they are not as easy to find as fast chargers.
The future of batteries
The future of electric car batteries is bright. Researchers are working on several technologies that could change the way we view electric cars. Some of the most interesting developments include:
- Solid-state batteries : As I mentioned before, these batteries could be a revolution. If researchers manage to solve some of the current problems, we could see cars with ranges of over 1000 km and much shorter charging times.
- Battery recycling : A major challenge is what to do with batteries when they reach the end of their life. Techniques are currently being developed to recycle battery materials more efficiently. Some manufacturers, such as Tesla, are already working on recycling programs to give used batteries a second life.
- Improving charging infrastructure : While charging infrastructure has improved greatly in recent years, there is still much work to be done. However, with massive investment by governments and private companies in creating networks of chargers, charging an electric car is likely to be as easy as filling up with petrol in the near future.
Conclusion
Batteries are the heart of electric cars and, although there is still a long way to go, technology has advanced a lot in recent years.
With increased range, improved charging times and new research into solid-state batteries, the future of electric cars looks bright. So if you're thinking about switching to an electric car, rest assured: batteries are more reliable than many think and will continue to improve over time.