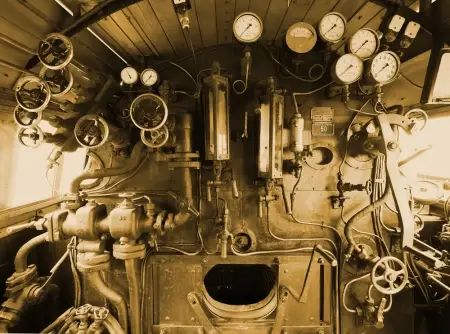
Steam engines were one of the most revolutionary inventions in history, playing a crucial role in the Industrial Revolution.
However, the use of these machines entails considerable risks, especially due to the high pressure and temperature at which they operate. Throughout history, numerous accidents have highlighted the importance of safety in the design, construction, and maintenance of these machines.
Below, we'll explore the key aspects of steam engine safety, from the basic principles to the modern devices and procedures that ensure their safe operation.
Operating principles and associated risks
Steam engines operate using the expansion of water vapor to generate mechanical motion. This process involves heating water to high temperatures in a boiler, which generates high-pressure steam. When this steam is released and directed toward a piston or turbine, it is converted into useful mechanical energy.
However, this basic principle also carries significant risks:
- Boiler explosions : If the internal pressure of the boiler exceeds its structural capacity, a catastrophic explosion can occur.
- Overheating and Cracking : Continued use can weaken materials, causing cracks that can compromise structural integrity.
- Safety valve failures : If these valves become blocked or fail, pressure can build up to dangerous levels.
- Burns and Steam Exposure : Operators and workers can suffer severe burns from contact with hot surfaces or escaping steam.
- Carbon monoxide leaks : In poorly ventilated boilers, incomplete combustion can generate toxic gases.
Safety devices in steam engines
Over time, various security mechanisms have been developed to mitigate these risks and ensure safe operation. Among the most important are:
1. Safety valves
Safety valves are essential for preventing overpressure in boilers. They operate by automatically releasing steam when the internal pressure exceeds a predetermined threshold. These valves must be checked periodically to prevent blockages or mechanical failures.
2. Pressure gauges
Pressure gauges allow operators to monitor the pressure inside the boiler in real time. Excessive pressure can be a sign of imminent danger, allowing corrective measures to be taken before an accident occurs.
3. Water level indicators
The water inside the boiler must be kept within a safe range. If the water level is too low, the boiler can overheat and be damaged; if it is too high, it can affect process efficiency. Level indicators allow operators to monitor these parameters.
4. Water injectors
Injectors allow the water inside the boiler to be replenished without interrupting its operation. This prevents water levels from dropping dangerously and keeps the temperature under control.
5. Automatic shut-off devices
Some modern machines incorporate automatic shutoff systems in the event of overpressure or overheating. These mechanisms can prevent serious accidents by stopping operation before the situation becomes critical.
6. Ventilation systems
Boilers must be well ventilated to prevent the buildup of dangerous gases. Proper ventilation systems prevent carbon monoxide buildup and improve combustion efficiency.
Safety regulations and standards
Given the dangers of steam engines, there are strict regulations governing their design, manufacture, and operation. Some examples include:
- ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers) Standards : These regulations establish design and testing requirements for boilers and pressure vessels.
- European regulations (PED - Pressure Equipment Directive) : Applicable in the European Union, they guarantee the safety of pressure equipment, including steam boilers.
- National regulations : Each country establishes specific regulations on inspections, maintenance and certification of steam equipment.
Compliance with these regulations is essential to prevent accidents and ensure the safety of workers and the environment.
Maintenance and good practices
Proper maintenance of steam engines is key to their safety and longevity. Some essential practices include:
- Regular Inspections : Periodically checking boilers and their components helps detect wear and tear or faults before they become a serious problem.
- Pressure tests : Pressure tests must be carried out to ensure that the boiler can withstand operating conditions without risk of explosion.
- Cleaning and descaling : Mineral deposit buildup inside the boiler can reduce its efficiency and increase the risk of overheating.
- Staff training : Operators must be well trained to identify danger signs and act quickly in case of emergency.
- Maintenance log : Keeping detailed records of all inspections and repairs allows for better control over equipment safety.
Historical accident cases and lessons learned
Throughout history, there have been numerous accidents involving steam engines. Some notable examples include:
- Sultana Explosion (1865) : A steamboat on the Mississippi River suffered a boiler explosion, killing more than 1,800 people. This disaster highlighted the need for stricter regulations on boiler maintenance.
- Thorold locomotive accident (1903) : A failure of the safety valve caused an explosion in a steam locomotive in Canada, leading to improvements in the regulation of exhaust valves.
- Manchester factory explosion (1850s) : Lack of proper maintenance and pressure buildup led to the destruction of a boiler, killing several workers and serving as a warning about the importance of regular inspections.