Steam machines can be classified into these two types:
- Plunger steam machine. This type of machine uses a piston or piston coupled to a crankshaft piston-connecting rod type mechanism. Within this type can be.
- Multiple expansion steam engine
- Uniflow or uniform flow motor
- Turbine steam machine
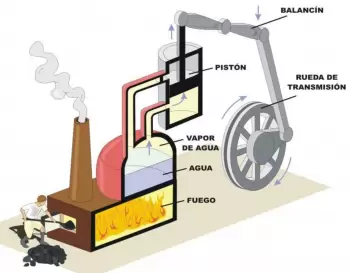
A steam engine is an external combustion engine capable of transforming heat energy into mechanical energy on a rotating axis. This heat energy takes advantage of the energy contained in water vapor at high pressure and temperature.
We consider steam machines all those machines that transform the thermal energy of a fluid into mechanical energy. In general, the fluid must be preheated and the outlet of the steam machine must be cooled to repeat the process.
These types of machines are the result of the improvements that James Watt made to the Thomas Newcomen machine. Subsequently, the steam engine, which would be essential in the development of the first Industrial Revolution.
Plunger steam machine
Plunger steam engines are the first steam engines developed using a plunger or piston coupled to a crankshaft piston-connecting rod type mechanism. To this mechanism steam was applied at high pressure and temperature synchronized with a set of valves to obtain kinetic energy and, therefore, mechanical movement.
How does a plunger steam machine work?
Water vapor is generated in a steam generator such as a boiler. Steam is introduced into a chamber where there is a control valve. This control valve is synchronously actuated by a mechanism coupled to the crankshaft of the machine. The displacement movement of the control valve causes the inlet chamber, where the supply steam is, to communicate alternately, to the top or bottom of the piston.
Steam pushes the plunger in both directions to rotate the crankshaft. At the same time, this control valve establishes communication on the opposite side of the piston, to the outlet duct to let out cold and useless low pressure steam. The temperature and pressure of the outlet steam are not high enough to continue taking advantage of its energy in this type of machine.
How is best performance achieved by multi-stage machines?
This elemental steam engine is very inefficient. The steam poured outside is still hot and at enough pressure to do more useful work. Multi-stage machines are used to improve the efficiency of this type of steam machine. In multi-stage machines, waste steam from one stage is fed into another with a larger piston to further utilize the energy it contains.
Steam from one stage is introduced into the next to drive an increasingly larger piston. In this way, the energy of the final output steam has been fully exploited.
This increase in piston size is necessary so that each stage of the steam engine can deliver approximately the same driving force. It must be considered that each time the steam has less pressure. Increasing the size of the plunger increases its surface. According to the laws of physics, the thrust force is the product of the pressure, per the area of the piston.
Within the piston machines we highlight the following types:
- Multiple expansion steam engine.
- Uniflow or uniform flow motor.
How does the multiple expansion steam engine work?
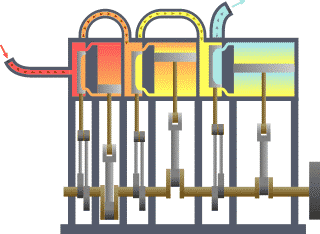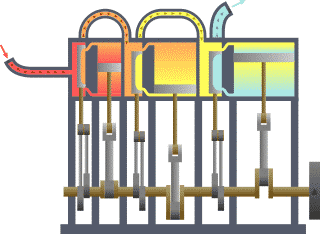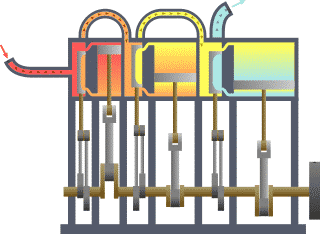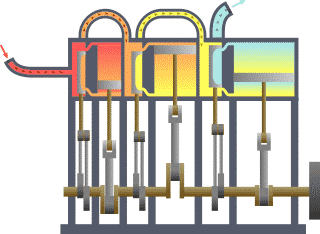
The multiple expansion steam engine is another type of steam engine. This engine uses multiple single-acting cylinders. Each cylinder has a larger diameter and movement than the previous one.
With the high pressure steam from the boiler the first piston, the piston with the smallest diameter, is pushed down.
In the upward movement of the first piston, the partially expanded steam is actuated within a second cylinder that is beginning its downward movement.
Lowering the second piston generates a further expansion of the relatively high pressure released in the first chamber.
Also, the intermediate chamber discharges to the final chamber, which in turn is released to a condenser. A modification of this type of engine incorporates two smaller pistons in the last chamber.
The characteristics of this type of steam engine made it an optimal engine for use on steam ships. The advantage was that the condenser, by recovering a little of the power, converted the steam back into water that could be reused in the boiler.
Land steam engines this advantage was not so important. Land machines could exhaust much of their steam and be refilled from a freshwater tower, but at sea this was not possible.
Before and during World War II, the expansion engine was used in marine vehicles that did not need to go at high speed. However, when more speed was required, it was replaced by the steam turbine.
How does the uniflow or smooth flow motor work?
Another type of plunger machine is the uniflow or uniform flow motor. This type of engine uses steam that only flows in one direction in each half of the cylinder.
The thermal efficiency of this steam engine is achieved by having a temperature gradient across the cylinder. Steam always enters through the hot ends of the cylinder and exits through openings in the center of the cooler. In this way, the relative heating and cooling of the cylinder walls is reduced.
In uniflow steam engines, the steam inlet is usually controlled by stem valves that are actuated by a camshaft. Stem valves operate similarly to those used in internal combustion engines.
The inlet valves open to admit steam when the minimum expansion volume is reached at the start of movement.
At a certain point in the turn of the crank, steam enters and the inlet of the bush is closed, allowing the continuous expansion of the steam. The entrance of the steam allows to actuate the piston transmitting a certain kinetic energy to it.
At the end of the movement, the piston will discover a ring of exhaust holes around the center of the cylinder. These holes are connected to the condenser. This action will lower the pressure in the chamber causing a quick release. The continuous rotation of the crank is what moves the piston.
Turbine steam machine
Turbine steam engines are the next evolutionary step of piston machines.
The main uses of turbine steam machines are:
- Generation of electricity. Turbine machines have a high operating speed that makes them ideal for driving an electric generator. These types of machines are currently used in nuclear power plants or thermal power plants. Less frequently they are also used in the field of solar energy in solar thermal power plants.
- Marine propulsion engines: It is an engine used in submarines, which makes use of high pressure steam to take water through an inlet located in front, and then expel it at high speed from the rear.
The old steam engines have been giving way to the turbines. Turbine steam engines improve durability, safety, relative simplicity, and are more efficient.
The turbine receives a jet of water vapor at high pressure and temperature. This jet of steam is suitably incident on a propeller with blades with a certain section. During the passage of steam between the propeller blades, it expands and cools, delivering the energy and pushing the blades to rotate the propeller placed on the turbine output shaft.
High-powered steam turbines use a series of rotating discs that contain a kind of propeller-type blades on their outer edge. These moving discs or rotors alternate with stationary rings or stators, attached to the turbine structure to redirect the flow of the steam. With this mechanism a very high speed of rotation is obtained.
Due to the high speed the turbines are normally connected to a reducer to convert the kinetic energy into power. The reducer is connected to another mechanism such as a ship's propeller.
Steam turbines require less maintenance and are more durable than piston machines. The rotational forces they produce are softer on their output shaft, contributing to less wear and less maintenance.
Where are turbine steam machines used?
The main use of steam turbines is in electricity generation stations. In this type of application, its high speed of operation is an advantage and its relative volume is not a disadvantage. Both in the fields of thermal power plants and nuclear energy this type of steam engine is used. Virtually all nuclear power plants generate electricity by heating the water and powering steam turbines.
Another application of turbine steam engines is the drive of large ships and submarines. These boats make use of high pressure steam to take water through an inlet located in front, and then expel it at high speed from the rear.