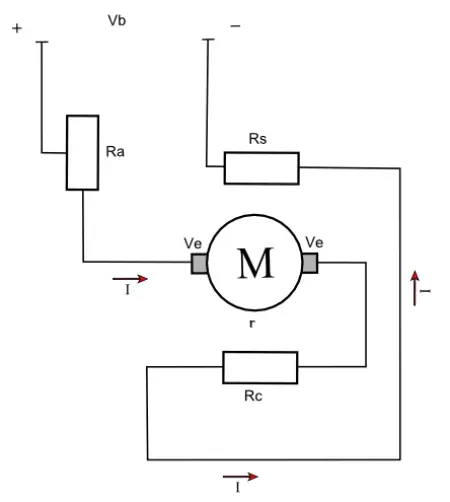
The series motor is a type of direct current (DC) electric motor widely used in a variety of applications due to its ability to generate high starting torque and its versatility in environments where power demand varies considerably.
This motor is characterized by having the armature and inductor windings connected in series, which implies that the current that flows through both is the same.
Next, its characteristics, operating principles, advantages and disadvantages, as well as its most common applications, will be expanded upon to provide a complete understanding of this type of engine.
Operating principle of the series engine
In the series motor, both the armature winding and the inductor are connected in series, meaning that the current flowing through the inductor is the same as the current flowing through the armature. When current is supplied to the motor, it passes through both components, creating a magnetic field in the inductor that interacts with the field generated in the armature. The interaction between these magnetic fields is what produces the rotary motion.
The torque generated by the series motor is proportional to the product of the magnetic flux and the current flowing through the armature. Since the magnetic flux also depends on the current passing through it, the relationship between the torque and the current is quadratic, which explains why this type of motor is capable of producing a high starting torque, even when the current is low.
One of the most important aspects of the series motor is that its speed varies depending on the applied load. As the load decreases, the speed tends to increase considerably, which can lead to overspeed problems when the motor is under no load. This particular behavior makes the series motor suitable for certain specific applications, but unsuitable for others, as we will see later.
Series engine features
The series excitation motor has a number of features that distinguish it from other types of DC motors, such as the shunt excitation motor and the compound excitation motor. These features make the series motor particularly useful in applications requiring powerful starting and the ability to adapt to variations in load.
High starting torque
The series motor is known for its ability to generate very high torque at start-up. This is because when the motor is stopped, the current passing through the inductor is maximum, which generates a strong magnetic field and, consequently, a high torque. This feature makes the series motor ideal for applications where it is necessary to start with a heavy load, such as in locomotives, trams, cranes and elevators.
Variable speed
The speed of a series motor varies considerably depending on the load it is carrying. When the motor is running at no load, its speed can increase dangerously, as the current in the inductor winding decreases, reducing the magnetic field and increasing the speed. This overspeed phenomenon can be detrimental to the motor and the system in general, limiting its use in applications where the motor could operate at no load.
Risk of overspeed
Due to the relationship between magnetic flux and current, when the series motor is operating without load, the speed can increase exponentially. This can be a danger to both the motor and the equipment connected to it, since the lack of load implies a low current in the inductor and, therefore, poor speed control. For this reason, series motors are not suitable for applications where the motor may frequently operate without load.
Almost constant power
Despite the variability in the speed of the stock engine, the power delivered by this engine tends to remain almost constant at different speeds. This is because any increase in engine speed also causes a reduction in torque, which compensates in terms of net power. However, this feature is useful only in applications where constant power needs to be maintained under different load conditions.
Stability against voltage variations
One of the advantages of the series motor is its ability to handle variations in the supply voltage. Since the current flowing through the inductor and the armature is the same, an increase in voltage generates an increase in current, which in turn increases both the magnetic flux and the induced electromotive force. This phenomenon helps to stabilize the absorbed current and to maintain the operation of the motor in relatively stable conditions against fluctuations in the supply voltage.
Advantages of the series engine
The advantages of the series excitation motor are remarkable, especially in industrial and transport applications. The main ones are highlighted below:
- High starting torque: As mentioned, one of the main advantages of this motor is its ability to generate high starting torque, making it the preferred choice for applications that require moving large masses from rest.
- Robustness and simplicity in design: Series motors typically have a simple and robust construction, which makes them easy to maintain and prolongs their service life, especially in industrial environments where conditions can be harsh.
- Adaptability to load variations: This motor adapts well to changes in load, making it suitable for applications where working conditions vary constantly, such as in electric traction systems.
- Relatively low cost: Compared to other types of DC motors, the series motor is relatively inexpensive, both in terms of purchase and maintenance, making it an attractive option in many industrial and transportation applications.
Disadvantages of the stock engine
Despite its advantages, the stock motor also has some disadvantages that must be taken into account when selecting it for a specific application:
- Idle instability: The main disadvantage of this engine is its instability when running without load. The overspeed that can occur under these conditions can be dangerous for both the engine and the systems around it.
- Difficulty in speed control: Precise speed control on a series motor is difficult due to its variable speed nature. In applications requiring fine speed control, this type of motor may not be the best choice.
- Limitations in applications with variable load: Although the series motor is capable of handling load variations, its behavior can be unpredictable in applications with rapid and frequent changes in load, which can result in operational problems.
Uses and applications of the series engine
The series motor is widely used in applications where high starting torque and the ability to adapt to changes in load are required. Below are some examples of common applications:
Electric traction
 Series motors are especially useful in electric traction applications such as trams, trains and other rail vehicles. In these cases, high starting torque is crucial to moving the vehicles from rest, and the ability to adapt to load variations is essential to handle changes in terrain gradient and passenger loads.
Series motors are especially useful in electric traction applications such as trams, trains and other rail vehicles. In these cases, high starting torque is crucial to moving the vehicles from rest, and the ability to adapt to load variations is essential to handle changes in terrain gradient and passenger loads.
Cranes and lifts
In industrial settings, series motors are often used in cranes, elevators, and other lifting equipment. These applications require a motor that can generate high torque at start-up to lift heavy loads, and the variable speed of the series motor allows performance to be adjusted based on the load.
Old electric vehicles
Although alternating current (AC) motors have gained popularity in modern electric vehicles, early electric vehicles and some heavy-duty vehicles still use production motors due to their ability to generate high torque at low speeds.
Examples of inappropriate applications
Despite its advantages in certain applications, the series motor is not suitable for all situations. For example, it is not recommended for use in portable power tools such as drills or saws due to the risk of overspeed when the motor is operating without load. If, for example, a drill using a series motor finishes drilling, the lack of resistance can cause the speed of the drill bit to increase dangerously, potentially putting the operator's safety at risk.