
The universal motor is a type of electric motor that can operate with both direct current and single-phase alternating current, which is why they are called universal.
These electromechanical devices are used in a variety of applications, from household appliances to power tools. Their versatility and efficiency make them a popular choice in many industries.
In general, they are very simple and economical motors that offer excellent starting torque and can reach very high rotation speeds.
What is a universal motor?
A universal motor is a type of electric motor designed to operate on both direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC). Its construction and operating principle are similar to those of a series-excited DC motor, allowing it to be adapted to both types of current without modification.
The universal motor consists of a stator with field windings and a rotor with a commutator and brushes. When current is applied, a magnetic field is generated in the stator which interacts with the rotor, producing the turning motion.
Its design allows it to reach high speeds, even higher than other types of electric motors of similar size.
Parts of a universal motor
Universal motors consist of several key parts that work together to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. These parts include:
- Rotor : The rotor is the rotating part of the motor and is also known as the armature. It is composed of a shaft and a set of coils or wire windings wound around the shaft. The rotor is the moving part of the motor that spins when electrical power is applied.
- Stator : The stator (or inductor) is the stationary part of the motor and surrounds the rotor. It contains permanent magnets or wire windings that generate a magnetic field when electrical power is applied. This magnetic field interacts with the rotor's magnetic field, causing the rotor to spin.
- Commutator : The commutator is a rotary switch mounted on the rotor that reverses the direction of the electric current in the rotor coils as it spins. This ensures that the rotor is always facing the correct direction and keeps spinning.
- Brushes : Brushes are small pieces of conductive material, usually carbon, that are in contact with the commutator. Brushes allow current to flow from the power supply to the rotor through the commutator, which generates the rotary motion.
- Housing : The housing is used to hold the parts that make up the stator. Normally aluminum or steel is used for its manufacture.
How does a universal motor work?
When a power supply is applied, current flows through the brushes, which make contact with the commutator. From there, the current is distributed to the rotor coils, generating a magnetic field around them.
This magnetic field interacts with the stator's magnetic field, causing a force on the rotor, according to Lorentz's law, which describes how a current-carrying conductor within a magnetic field experiences a force that drives it to move.
To maintain rotation, the commutator constantly reverses the direction of the current in the rotor coils as it spins. This ensures that the magnetic attraction and repulsion between the rotor and stator remain in the same direction, allowing for continuous motion.
Thanks to this mechanism, the universal motor can operate with alternating or direct current without requiring changes to its structure, achieving high operating speeds and versatile performance in various applications.
Universal motor diagram
The universal motor diagram is as follows:
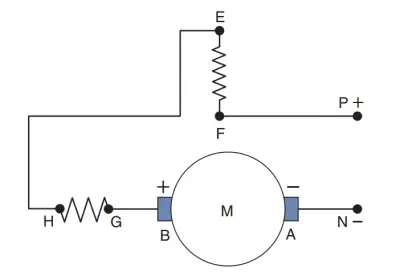
Main Features
Universal motors have several characteristics that make them stand out in various applications:
High speed
Universal motors are known for their high rotation speed, making them suitable for applications requiring fast speeds, such as power tools and household appliances.
The speed is directly proportional to the current, if the direction of the current is reversed, the direction of rotation is reversed.
Unlike asynchronous motors, the rotor of the universal motor rotates at the same speed as the stator's magnetic field.
High torque
These motors can also generate very high starting torque, making them ideal for starting heavy loads, such as those found in vacuum cleaners or drills.
Variable efficiency
The efficiency of a universal motor can vary depending on the load and speed. At light loads, they can be quite efficient, but their efficiency can decrease at heavy loads.
This type of engine is not built for use over long periods of time.
Compatibility with alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC)
The ability to operate on both types of electrical current makes them versatile and suitable for a variety of applications and environments.
In alternating current it behaves in a similar way to a direct current series motor and the power is lower than when it does so in direct current.
Simplicity
The electrical circuit is very simple, it has only one path for the current to pass through, because the circuit is connected in series.
Types of universal motors
While all universal motors share fundamental characteristics, there are different types depending on their design and specific applications.
Some of the most common types include:
Universal motors series
These motors have a series design where the rotor and stator are connected in series. They are suitable for applications requiring high torque and variable speeds, such as power tools.
Universal compound motors
Compound motors combine elements from series motors and shunt motors. They have a good balance between speed and torque and are used in applications such as fans and sewing machines.
Universal shunt motors
These motors have the rotor and stator connected in parallel (shunt). They are ideal for applications requiring constant speeds, such as ceiling fans and blenders.
Universal electronic commutator motors
Some modern universal motors use electronic rather than mechanical switches to reverse the direction of current. This improves efficiency and reduces wear on mechanical parts.
Application examples
The use of these alternating current motors is widespread due to the greater starting torque compared to induction motors and their high rotation speed, which allows their size and price to be reduced.
The universal motor is undoubtedly the most widely used electric motor in the household appliance and portable tool industry. It is also used in other applications where high rotation speed is required with low loads or small resisting forces.
Everyday examples
Some examples of applications where universal motors are used include:
-
Household appliances: They are used in vacuum cleaners, blenders, hair dryers and ceiling fans due to their ability to deliver variable speeds and high torque.
-
Power Tools: Drills, circular saws, and angle grinders are examples of tools that often incorporate universal motors due to their ability to handle variable loads.
-
Kitchen Appliances: Hand mixers and blenders use universal motors to mix and blend foods with ease.
-
Ceiling Fans: Universal shunt motors are ideal for these devices as they can maintain a constant speed.
-
Sewing Machines: Electric sewing machines often use universal motors because of their ability to provide precise speed and control.
-
Portable Tools: Some portable tools such as sabre saws and sanders also use universal motors.