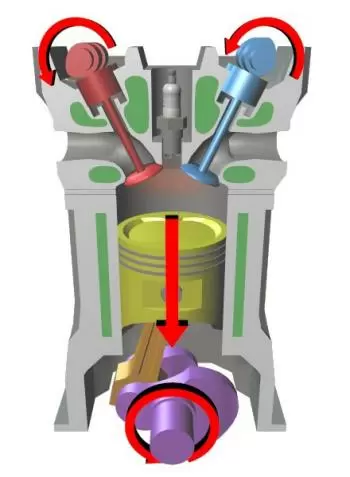
A four-stroke engine is an internal combustion engine that performs four piston strokes in each cycle while the crankshaft performs two full revolutions.
This type of engine can work both in the diesel cycle and in the Otto cycle (gasoline engine).
These four times are: intake, compression, combustion or explosion, and exhaust. We explain them in more detail below:
Admission of the load in the cylinder
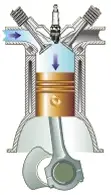 The piston goes down, drawing in the air-fuel mixture once the intake valve is open. The valve begins to open before the stroke begins and closes after the stroke is completed. The exhaust valve remains
The piston goes down, drawing in the air-fuel mixture once the intake valve is open. The valve begins to open before the stroke begins and closes after the stroke is completed. The exhaust valve remains
The crankshaft makes half a turn and the camshaft rotates 90º.
Compression of the load in the cylinder

The piston reaches the lower end of the stroke and the intake valve closes. At this moment, the piston rises again compressing the gas contained in the chamber. The crankshaft rotates 360º and the camshaft rotates 180º, and also both valves are closed and their stroke is upward.
The volumetric compression ratio is the volume of the load at the end of the stroke. This value is reduced to a fraction of its original volume.
Combustion and expansion
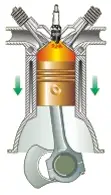
At this point the gas is at maximum pressure and the ignition is carried out in a different way depending on the combustion cycle used:
-
In gasoline engines, the spark jumps at the spark plug, causing the compressed mixture to ignite.
-
In diesel engines, fuel is injected that ignites itself by the existing pressure and temperature.
In both cases, the combustion causes an increase in temperature and the gases expand pushing the piston, generating mechanical work. During lowering the intake and exhaust valves are closed.
During this time, the crankshaft turns half a turn while the camshaft turns 240º.
Before the working stroke is completed, the exhaust valve begins to open and the combustion gases begin to escape.
Expulsion or escape of combustion products
 The piston rises and pushes the combustion gases that come out through the exhaust valve.
The piston rises and pushes the combustion gases that come out through the exhaust valve.
Upon reaching the upper limit switch, the exhaust valve closes and the intake valve opens to restart the cycle.
During this time, the crankshaft performs a complete rotation and the camshaft rotates half a turn.