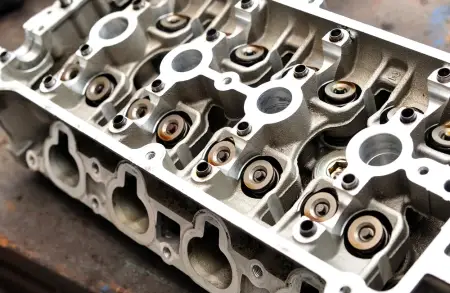
A cylinder head is a fundamental part of internal combustion engines, as it forms the upper closure of the engine block and allows the combustion chambers to be sealed.
Furthermore, it is the structure on which key components such as valves, spark plugs (in spark ignition engines) or injectors (in diesel engines) sit, all of them with holes specifically designed for this purpose.
Main function of the cylinder head
The cylinder head performs the important function of hermetically sealing the engine block. In internal combustion engines, especially those with the Otto cycle (spark ignition) and diesel cycle (compression ignition), the cylinder head contains and defines the geometry of the combustion chamber. It is fixed to the block by means of screws or studs and, inside, houses a series of mechanisms essential to the operation of the engine, such as the valves, the ignition and injection systems, and the intake and exhaust manifolds.
In 4-stroke engines, the cylinder head also integrates valve actuation systems, which gives it an essential role in the correct synchronization of the entry and exit of gases. In addition, it has channels for the circulation of the coolant, which helps maintain the optimum operating temperature.
Manufacturing materials
The cylinder head is made mainly from aluminium alloys , a material that stands out for its low density and excellent thermal conductivity, which allows the heat generated during combustion to be efficiently evacuated.
In high-performance engines, special alloys are also used to ensure greater resistance to thermal and mechanical stress. On the other hand, in smaller-capacity engines, such as 2-stroke engines (for example, in small-capacity motorcycles), the cylinder head is usually simpler and, in many cases, air-cooled.
Cylinder head gasket
The cylinder head gasket is a key component in the engine sealing system. It is made from composite materials, such as synthetic fibres, which replace traditional asbestos, a material previously used but now banned due to its health risks.
Its main function is to ensure a perfect seal between the cylinder head and the engine block, withstanding the high pressures and temperatures generated inside the engine.
Cylinder head design
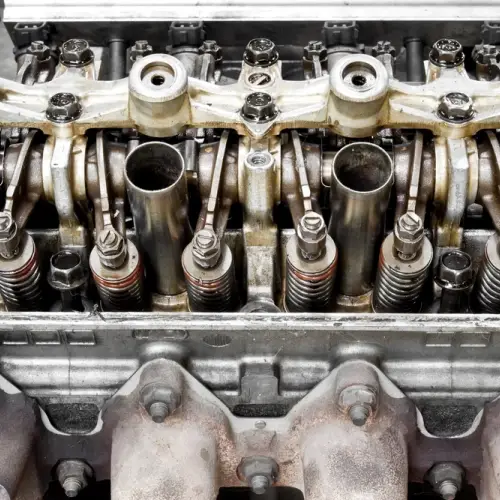 Cylinder head design must take into account several factors to ensure optimum engine performance. These factors include:
Cylinder head design must take into account several factors to ensure optimum engine performance. These factors include:
- The thermal field : the cylinder head is exposed to large thermal variations. Areas close to the flame plane, where temperatures can exceed 250°C, are particularly critical, as hot spots can generate mechanical stresses and cracks.
- Gas flow distribution : The design of the cylinder head directly affects the intake and exhaust gas flow. An efficient design improves engine performance and reduces fuel consumption.
- Stress analysis : This is carried out using simulations that model the thermal and mechanical loads to which the cylinder head is subjected during operation, evaluating its strength and durability.
The design of the cylinder head is crucial to optimizing combustion and overall engine performance, determining aspects such as the shape of the combustion chamber, the passage of intake and exhaust gases, and the location of the valves and their actuation mechanisms.
Conclusion
In short, the cylinder head is not only an essential structural component in the internal combustion engine, but it also has a direct impact on engine performance. Its design and manufacturing material must be carefully selected to withstand extreme temperature and pressure conditions, ensuring efficient and long-lasting engine operation.